How to set the timezone for your GitHub Codespaces
This post is over a year old, some of this information may be out of date.
A couple of days ago, someone opened an issue for Front Matter CMS about the auto-update of the modified date in their articles that did not follow the date format. In the issue, they shared a video recording of the problem. I noticed that GitHub Codespaces was used. GitHub Codespaces provides you with a cloud-based development environment for your repository.
When I looked into the issue, I noticed it was related to the fact that the GitHub Codespace uses UTC/GMT as its time zone. You can verify this by running the date command in the GitHub Codespace terminal.

You can also check the timezone by running cat /etc/timezone in the terminal.

Because the GitHub Codespace uses UTC as its time zone, the date formatting on the server side did not follow the user’s timezone (+07:00), resulting in an incorrect date in the article.

To overcome this issue, I looked into how to set the timezone for the GitHub Codespace. The solution I found is to set the TZ environment variable, which will be explained in the following steps.
Setting the timezone for GitHub Codespaces
There are a couple of ways to set an environment variable for a GitHub Codespace:
- In the
.devcontainer/devcontainer.jsonfile in your repository - In the Codespaces secrets settings
- Using a custom Dockerfile
- Using a dotfiles repository
In this article, I will focus on the first two options.
Setting the timezone in the devcontainer.json file
When a GitHub Codespace starts, it uses a Docker container to run your development environment. The .devcontainer/devcontainer.json file configures the container.
When you do not have a .devcontainer/devcontainer.json file in your repository, you can manually create it or run the Codespaces: Add Dev Container Configuration Files... (command ID: github.codespaces.configureDevContainerCommand) command from the command palette.
Once you have the .devcontainer/devcontainer.json file, you can set the TZ environment variable in the remoteEnv property.
{ "remoteEnv": { "TZ": "Europe/Brussels" }}After you have saved the file, you can restart the GitHub Codespace to apply the changes. You can do this by running the Codespaces: Rebuild Container (command ID: github.codespaces.rebuildEnvironment) command from the command palette.
Once the GitHub Codespace has restarted, you can verify the timezone by running the date command in the terminal.

Setting the timezone in the Codespaces secrets settings
This method has the advantage of allowing you to apply environment variables to specific repositories without committing changes to the repository. This keeps the settings private and only available to you.
To set the timezone in the Codespaces secrets settings, you can follow these steps:
- Go to GitHub
- Open your profile settings
- Click on the Codespaces link under the “Code, planning, and automation” section
- Click on the New secret button
- Add the
TZenvironment variable with the timezone value (e.g.Europe/Brussels) - Select the repositories where you want to apply the environment variable
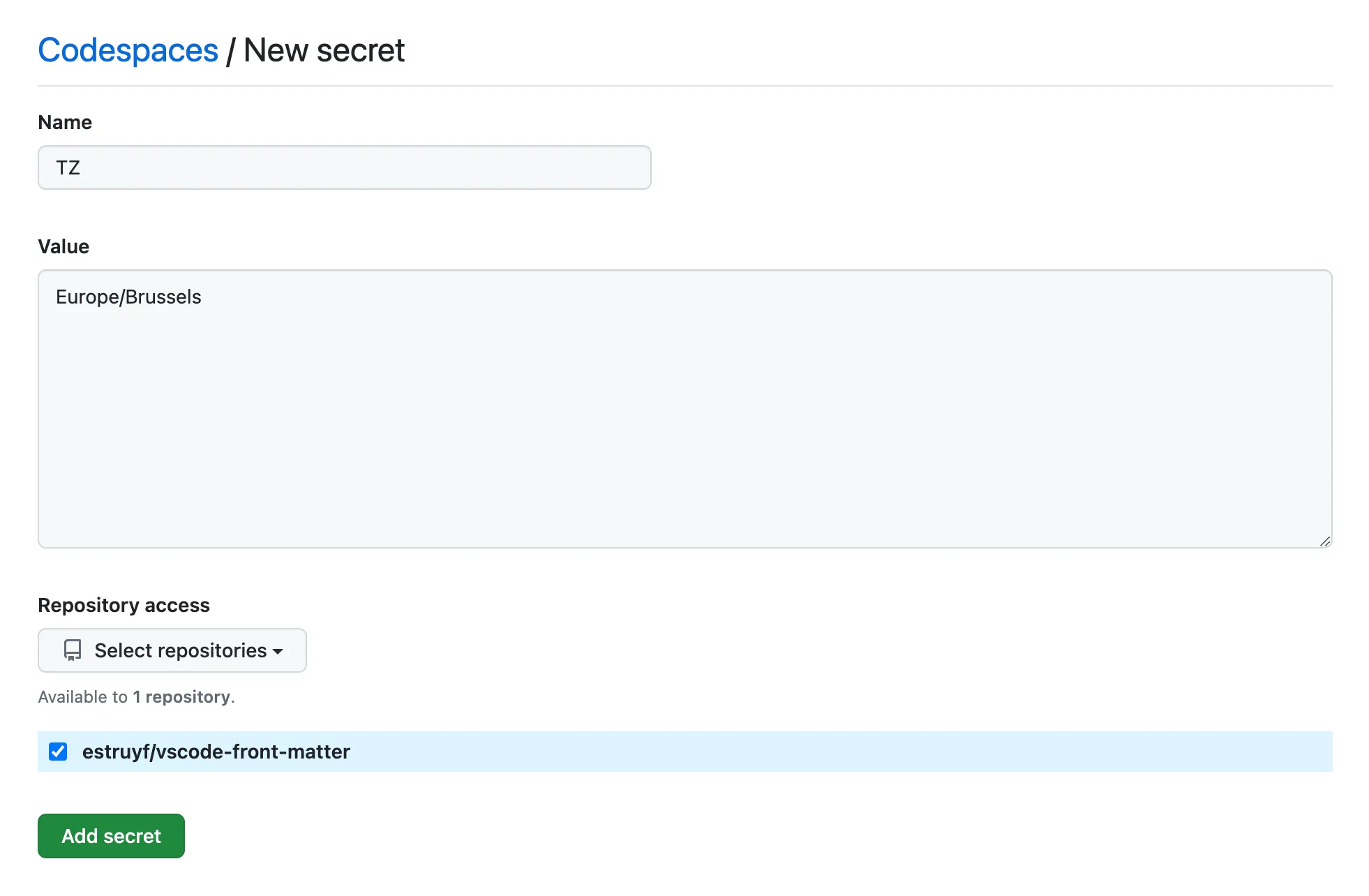
- Click on the Add secret button
After you have added the secret, you can restart the GitHub Codespace to apply the changes. To do this, run the Codespaces: Rebuild Container (command ID: github.codespaces.rebuildEnvironment) command from the command palette.
Once the GitHub Codespace has restarted, you can verify the timezone by running the date command in the terminal.

Related articles
Manual GitHub workflow triggers for Azure Static Web Site
Which service? Netlify vs Vercel vs Azure Static Web App
Running the CollabDays Benelux event on Azure Static Web App
Report issues or make changes on GitHub
Found a typo or issue in this article? Visit the GitHub repository to make changes or submit a bug report.
Comments
Let's build together
Manage content in VS Code
Present from VS Code
